Pentest black box vs grey box: which one to choose?
types of pentest black box vs gray box
When we talk about penetration testing (pentest), The choice of methodology largely determines the quality and relevance of the security results. Two approaches are particularly dominant in organizations: black box penetration testing and grey box penetration testing. Understanding their differences and respective strengths is essential for accurately assessing the security level of your infrastructure.
See also: cyber maturity assessment
Type of black box penetration test: simulation of an external attacker
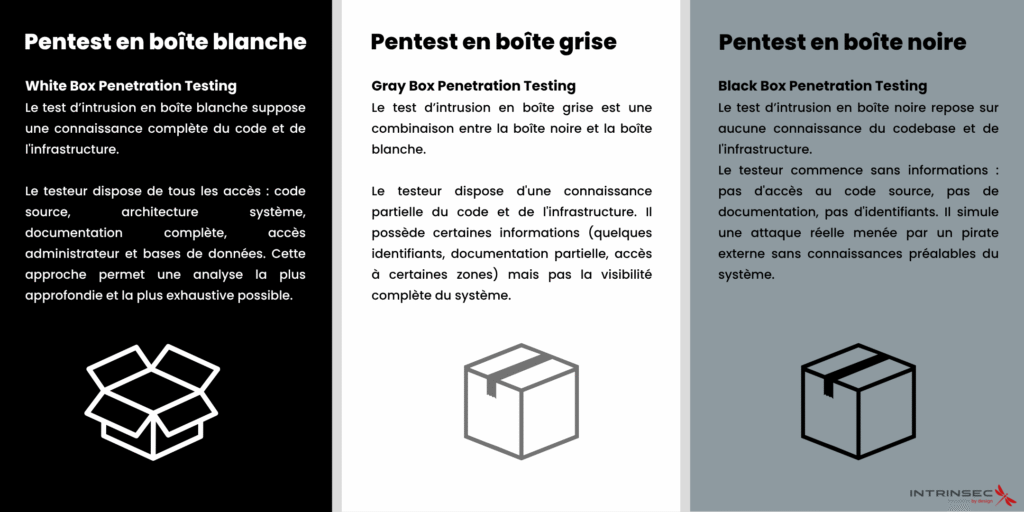
A black box penetration test simulates a real attack carried out by a cybercriminal with minimal access to the targeted system. The penetration tester starts without any information about the organization's architecture, configurations, source code, or security policies.
This approach places the auditor in the exact position of an external hacker seeking to compromise the system without prior knowledge. The tester must therefore explore, scan, and identify entry points independently, faithfully replicating the conditions of a real intrusion.
The forces of the black box
The main advantage of the black box pentesting lies in its maximum realism. Since hackers typically have limited information about the information system they are trying to compromise, this approach accurately reflects the real-world conditions of an attack.
This methodology allows security teams to reliably identify external vulnerabilities that could be quickly exploited by an attacker. The results highlight the most critical weaknesses and those immediately accessible from the outside.
The constraints of the black box
However, black box testing has practical limitations. Because the penetration tester dedicates time to exploration and reconnaissance, the test is generally longer and therefore more expensive. Furthermore, they cannot access the internal layers of the system to identify deeper vulnerabilities, which limits the scope of the audit.
See also: Technical Audit
Grey box type of pentesting: the pragmatic intermediate solution
The grey box pentester is positioned between the black box and the white box, providing the pentester with a limited set of information on the targeted system. This intermediate approach offers a concrete starting point while maintaining a realistic threat aspect.
During a grey box test, the penetration tester may receive user accounts with restricted rights, partial documentation on the architecture, access to certain client interfaces, or credentials allowing them to bypass the authentication step. The goal is to simulate an attack carried out by a cybercriminal who has gained initial access to the system.
The advantages of the grey box
The grey box corresponds to the most realistic threat that organizations actually encounter. The majority of attacks do not start from scratch: the hacker has partial information, a compromised user account, or accesses the system as a malicious employee.
This method allows testing efforts to be focused on priority risk areas, without wasting time on initial reconnaissance. It offers an excellent balance between threat representativeness and test effectiveness. The penetration tester can simulate various attack scenarios: access by employees, external contractors, or former employees.
The grey box also tests defense mechanisms in depth. Once initial access is obtained, the auditor assesses network segmentation flaws, insufficient access validation mechanisms, and the detection of actions initiated from misused legitimate accounts.
Points of vigilance regarding the grey box
The grey box does not detect completely external vulnerabilities that require thorough initial reconnaissance. If you need to validate the robustness of your first lines of defense against an attacker with no prior information, the grey box will not provide that assurance.
Which pentest should you choose based on your context?
The choice between black box and grey box depends closely on your security maturity and audit priorities.
Choose the black box type of pentesting
If you want to assess your defenses against a realistic attack from a completely external hacker, or if you've never performed a penetration test before, this approach ensures coverage of the most accessible and critical vulnerabilities.
Prefer the type of pentesting grey box
If you have already validated your first lines of defense, or if you are looking to simulate the most likely threats to your organization, the grey box is essential. the most frequently used methodology in business because it balances realism and pragmatism. It also remains valid for testing restricted access areas, client zones, or particularly sensitive functionalities.
In practice, many organizations combine the two approaches across different scopes, depending on the maturity of each area. This multi-approach strategy offers comprehensive coverage while optimizing audit resources.
About Us
Intrinsec stands out for its ANSSI official qualifications, attesting to our compliance with the most demanding regulatory, technical, and safety requirements of the French government. Our qualification PASSI LPM/RGS covers all critical audit areas: architecture, configuration, source code, penetration testing, and organizational and physical audits.
See also
Ready to Strengthen Your Cybersecurity?
Protect what really matters to your business. Our experts
cybersecurity experts will assist you in securing your
digital assets.







